Updated on July 3, 2025
Agentic AI is an advanced AI-powered automation tool that can perform tasks for you. LLMs like ChatGPT and Claude power these agents and can pull data and form different functions using multiple tools.
Usually, LLMs are limited by the training data and reasoning capabilities, but agentic AI for customer service uses tool calling to perform complex functions. For example, you can use it to reply to emails, automate customer interactions, and solve customer problems efficiently.
In this article, we’re going to discuss these AI machines, and we’re going to cover:
2. What are the types of Agentic AI?
5. Why is Agentic AI used for Customer Service?
6. How can you implement Agentic AI for your business?
7. Conclusion
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI represents a significant evolution in artificial intelligence, offering enhanced autonomy and decision-making capabilities beyond traditional AI systems. Unlike conventional AI, which relies on human instructions, agentic AI can independently perform complex tasks, adapt to changing environments, and pursue goals with minimal human intervention.
Generally, agentic AI consists of multi-agent orchestrations that can communicate with one another to complete a task. Let’s take the example of an agentic AI system for flight booking. One AI agent specializes in research, while another is trained and equipped to handle the booking process -managing card details, OTPs, security checks, and more. These two AI agents collaborate to complete a single task, and together, they form an agentic AI system.
This makes it a powerful tool across various industries, especially in the AI-driven customer service function. Agentic AI enhances automated workflows by handling inquiries, reducing response time, and personalizing support. To understand it better, let’s compare AI Agents with non-AI agents.
Agentic AI v/s Non-Agentic AI
| Category | Description |
| Agentic AI | A class of AI systems capable of autonomous action and decision-making. Unlike non-agentic AI, which reacts to inputs within predefined rules, these systems pursue complex goals and influence their environment independently. |
| Characteristics of Agentic AI | – Autonomy: Achieves complex objectives without requiring human collaboration. – Language Comprehension: Understands nuanced human speech and text effectively. – Rationality: Makes informed, contextual decisions using advanced reasoning engines. – Adaptation: Adjusts plans and goals in dynamic situations. – Workflow Optimization: Streamlines and organizes business workflows with minimal oversight. |
| Applications of Agentic AI | – Robotics: Manages inventory, predicts demand, and handles disruptions autonomously. – Customer Service: Enhances customer experience through personalized, proactive engagement. – Healthcare: Automates administrative tasks like scheduling and data management. – Human Resources: Supports recruitment and employee management at scale. |
| Challenges of Agentic AI | – Ethical considerations around decision-making transparency. – Accountability for actions taken independently. – Ensuring safety and addressing biases in data to prevent skewed outcomes. |
| Non-Agentic AI | Reactive AI systems are designed for specific tasks, operating within predefined rules and parameters. Lacks autonomy and decision-making capabilities. |
| Characteristics of Non-Agentic AI | – Excels in structured environments for automating repetitive tasks. – Follows programmed responses or rules. – Cannot independently analyze environments or adjust operations. |
| Limitations of Non-Agentic AI | – Inability to adapt to dynamic contexts. – Restricted to executing predefined tasks without nuanced decision-making capabilities. |
| Applications of Non-Agentic AI | – Finance: Processes transactions and assesses risks. – Customer Service: Uses chatbots for simple interactions. – General Automation: Handles data entry and scheduling tasks. |
| Comparative Analysis | – Agentic AI: Autonomous, proactive, and capable of complex decision-making. – Non-Agentic AI: Reactive, task-specific, and limited to predefined rules. – Agentic AI operates on an autonomy spectrum, requiring robust oversight and ethical safeguards. |
What are the Types of Agentic AI?
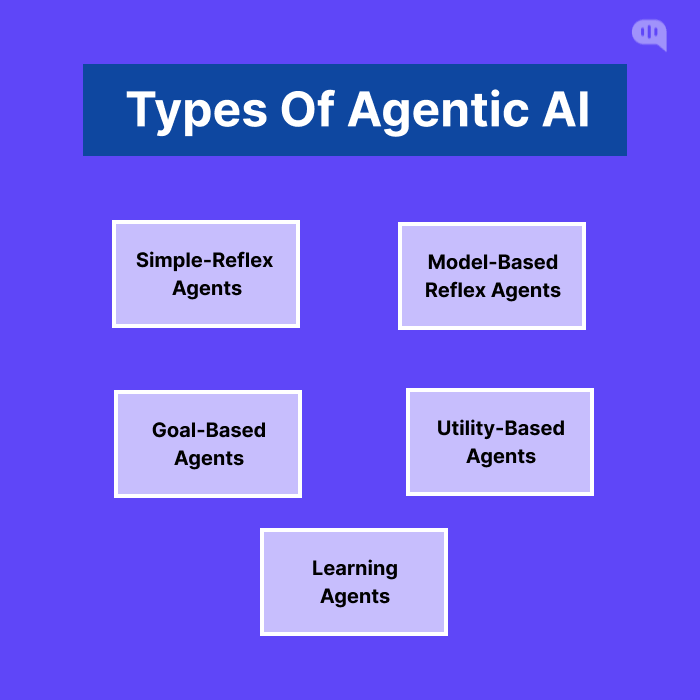
Agentic AI has different types of capabilities based on how they are programmed. They can be programmed to do basic tasks or complicated operations. These actions also inform the types of AI agents that we can build. These are:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
These are agents that react based on a specific trigger. They do not interact with other agents or do different actions. If they face an unknown situation, they can’t handle it.
For example, an AI agent that replies: “We’ve created a support ticket for you named #123XXX” whenever it receives a customer complaint.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
These agents can store memory and create internal models of the world as they perform actions. While they still perform simple actions, they can operate in unknown, partially observable environments. For example, a Tesla can use images of the outside environment to learn how it will drive.
3. Goal-Based Agents
These AI agents have memory and an internal goal (or a set of goals) to complete through multiple actions. These agents search for and perform the tasks needed to finish the goal. For example, Google Maps AI searches various routes to find the best path for your destination.
4. Utility-Based Agents
These agents are programmed to do actions that maximize the utility or reward for a particular action. For example, a code review tool that optimizes the memory that your product uses.
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents automatically add new knowledge into their models to improve the execution of different processes. These agents are utility- or goal-based and continuously evolve based on the environment in which they operate. For example, personalized recommendation chatbots on e-commerce sites constantly use customer data to develop and improve product recommendations.
How Does Agentic AI Work?
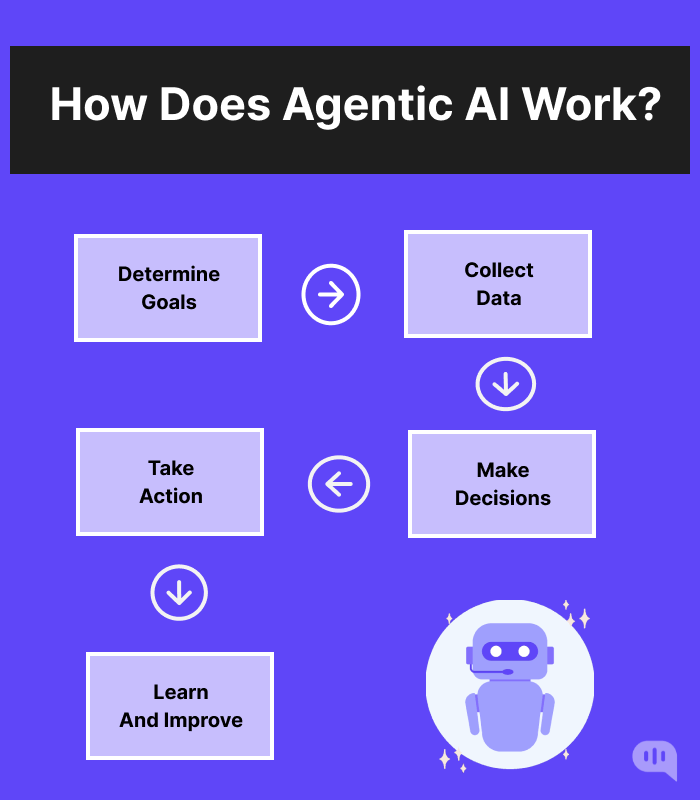
Much like a programmer, agentic AI executes tasks by breaking them into small parts and executing them well. This happens in the following order:
1. Determine Goals
Like any other tool, your agentic AI will start with instructions. This functions just like the intents for an AI chatbot, where you give instructions to the agent to follow throughout the task. You also set goals during this process, and the AI agent will try to fulfill these goals while they perform the task.
2. Data Collection
Agentic AI is used to collect data from different sources, continuously collecting data and becoming aware of the current environment. This data collection helps it understand the parameters that will influence the task. For example, Suppose the goal is to collect information about a customer and give them product recommendations. In that case, it will gather data from the CRM and see the customer’s regular purchases and buying behavior.
3. Decision-Making
Now, the AI agent has the data and instructions to break down the problem and decide what to do. For example- A navigational AI system will see GPS data and the traffic concentration to choose the optimal path for your vehicle.
4. Action Execution
The AI agent will go to work and perform different tasks to reach its goal. For example – An agentic AI for customer service might first collect data about the problem, read the documentation on how to solve the problem, collate that information, and then present it to your customer so they can solve it.
5. Learning and Adaptation
Agentic AI gets better with time based on the different kinds of feedback. So, your agents will learn about the environment and the feedback and improve themselves after every action they perform. As time passes, they can perform your tasks faster and more efficiently.
This process lets agentic AI add value to any business by automating repetitive tasks, leaving humans to concentrate on more complex issues. In customer service, for example, an AI agent can get customer information, store it in the CRM, raise a support ticket, and troubleshoot the user’s problem.

Where is Agentic AI Used?
Agentic AI is used in multiple sectors to improve efficient workflows, improve customer experiences, and automate complex tasks. Let’s look at some everyday use cases:
Healthcare
AI is used in Healthcare industry for patient monitoring and care management in hospitals and integrated healthcare facilities. Wearable and bio-medical devices track the patient’s status and provide data to your physicians so that they can provide timely care if something changes.
This is especially useful in Emergency Rooms during rush hours and in ICUs with many critical patients.
Education
Educational institutions use Agentic AI to help students in various ways. They can design their AI as co-pilots for application and examination registration processes.
Agentic AI is also helpful in personalizing course material based on the student’s performance and learning pace. These customized approaches improve performance and learning outcomes for students.
Transportation and Fleet Management
In a recent presentation about Robotaxis, Elon Musk remarked, “The autonomous future is here; with autonomy, you get your time back.”
He was referring to a group of robotaxis that he plans to launch shortly. Autonomous driving agentic AI can help ease the traffic burden and improve overall traffic movement. Tesla and Waymo have already demonstrated successful autonomous driving to people.
This success can be replicated in fleet management as well. AI agents that drive trucks and manage inventory and traffic will be beneficial in controlling the high-volume inventory movement across the U.S. Modern fleet platforms are evolving to support this shift, enabling real-time visibility and smarter operations at scale.
Finance and Banking
The NFSI sector has benefited a lot from agentic AI. They’ve employed these agents to provide customer service and improve operational efficiency.
These agents provide 24/7 customer support, personalize recommendations, and execute transactions. They also do tasks quickly, providing greater customer satisfaction overall.
Additionally, agentic AI is used in risk management and anti-money laundering cases, constantly examining data to find real-time anomalies.
Security
Agentic AI is integrated into security systems worldwide to understand and detect threats. These agents examine incoming data and try to identify suspicious elements or links that might threaten users’ security.
Complex and specific agents also help businesses manage databases and reduce cybersecurity risks.
Customer Service
Agentic AI in customer service has been widely adopted for automating customer query resolution and improving operational efficiency. These AI-powered agents can handle customer support automation, reducing workload while ensuring faster response times. With modern improvements, they can also perform small tasks on the server to streamline customer service operations and solve common customer problems.
Multiple sectors and functions are using AI agents for their ability to perform a diverse set of tasks. One of these crucial use cases is customer service, which cuts across sectors. Let’s look at what AI agents bring when used for customer service.
Why is Agentic AI Used in Customer Service?
Agentic AI provides a lot of benefits to customer service functions:
1. 24/7 Availability: These agents are built to provide scale to customer support functions. They are available round-the-clock and can handle multiple simultaneous inquiries.
2. Cost Reduction: These agents save money by automating low-risk and repetitive queries, minimizing the need for extensive human intervention. This lowers operational costs and enhances accuracy and efficiency across critical marketing and customer management workflows. Moreover, organizations can benefit from reduced labor costs by automating repetitive tasks, leading to significant long-term savings.
3. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: One of the most significant advantages of agentic AI is its ability to automate routine tasks, allowing employees to focus on more complex and higher-value work. This automation leads to enhanced productivity, as AI can perform tasks with speed and accuracy that surpass human capabilities, thereby reducing the incidence of human error.
4. Improved Customer Experience: Integrating agentic AI into customer service strategies has revolutionized customer interactions. By providing personalized insights into customer preferences and past behaviors, AI agents enhance the quality of interactions and foster a customer-centric support system. This personalization has improved customer satisfaction, as clients feel valued and understood. Moreover, AI systems can proactively identify potential issues, enabling organizations to address problems before they escalate, thus maintaining a smooth operational flow.
Enhance support workflows, accelerate resolutions, and boost efficiency with AI-powered email ticketing from KommunicateHow to Implement Agentic AI for Business?
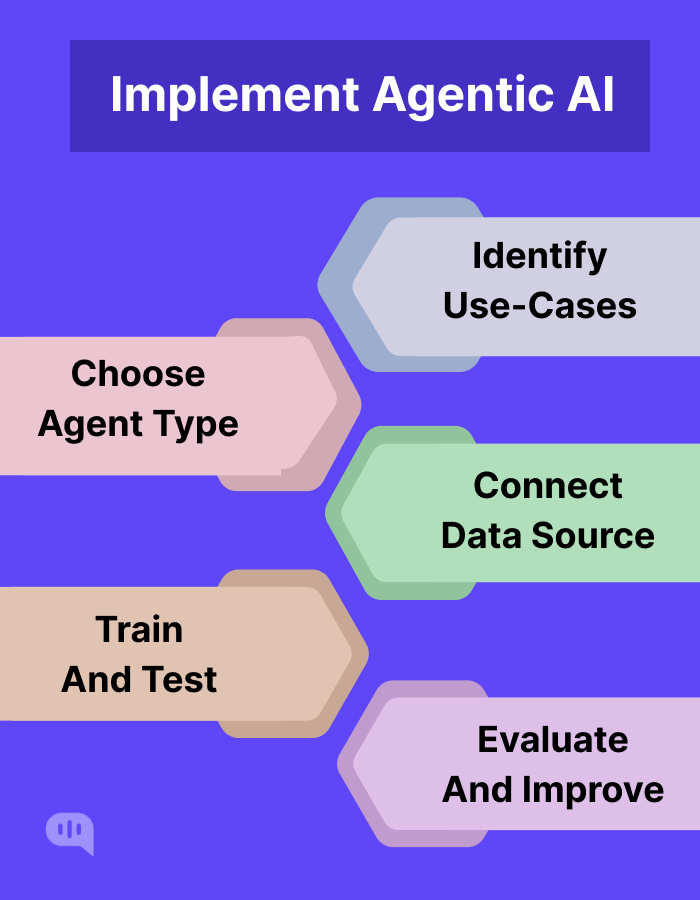
Agentic AI is usually implemented through the following process:
1. Identifying Use Cases
The first step in implementing agentic AI is identifying the most appropriate use cases where intelligent agents can provide significant value. Organizations should assess their pain points, repetitive tasks, and data-intensive processes to determine areas that would benefit from automation or enhanced decision support.
Engaging stakeholders from various departments helps gather insights and requirements, ensuring that the selected use cases align with the organization’s overall goals and strategy. For instance, process automation, customer service, and decision-making support are common targets for these deployments.
2. Selecting Agent Types and Architectures
Once potential use cases are identified, the next step is to select the most suitable types of agentic AI and its architecture. This selection depends on the complexity of the tasks, the level of autonomy required, and the available data resources.
3. Preparing to Connect Data
You need to provide access to agentic AI so that it can gather and connect enterprise data. This involves the evaluation of the organization’s data infrastructure, ensuring data availability and quality, and establishing protocols for data access. An effective integration with existing systems will enhance the agent’s ability to function autonomously, process real-time information, and make informed decisions.
4. Training and Learning
Agentic AI benefits significantly from continuous learning and improvement. Unlike traditional automation tools, which follow static rules, these agents can adapt based on interactions and outcomes. Organizations should establish mechanisms for ongoing training and updates to refine the agents’ capabilities over time. This could involve machine learning techniques to continuously analyze performance data, user interactions, and environmental changes to optimize the agents’ functions.
5. Testing and Evaluation
Before full deployment, rigorous testing of agentic AI is essential to ensure it functions as intended and meets performance expectations. This phase may involve simulated environments and real-world pilot projects to evaluate the agents’ effectiveness in accomplishing designated tasks. Feedback from users during this phase is invaluable for making necessary adjustments and enhancements.
Organizations can implement agentic AI by following these steps, transforming operations and enhancing overall efficiency.

Conclusion
Agentic AI is revolutionizing various industries by combining advanced autonomy, decision-making capabilities, and efficiency. From healthcare to transportation, education, finance, and especially customer service, these intelligent systems automate repetitive tasks, enhance productivity, and personalize interactions, improving operational outcomes and customer satisfaction.
Their ability to learn and adapt over time ensures continuous improvement, while their scalable nature offers cost-saving opportunities for businesses of all sizes. However, implementing agentic AI requires thoughtful planning, from identifying use cases to rigorous testing and evaluation, ensuring seamless integration with existing workflows.
As the technology evolves, the potential of agentic AI to transform industries continues to grow. By leveraging their capabilities responsibly, businesses can unlock new opportunities, streamline operations, and deliver exceptional value to customers, setting the stage for a more efficient, intelligent future.

CEO & Co-Founder of Kommunicate, with 15+ years of experience in building exceptional AI and chat-based products. Believes the future is human + bot working together and complementing each other.