Updated on January 10, 2025

Ticket Triage in Customer Support is the process that businesses use to prioritize customer inquiries. Ticket Triage helps the customer support team to manage a high volume of support tickets.
Ticket Triage categorizes issues, assigns resources, and addresses urgent matters. You will also be optimizing customer support operations and enhancing customer experience.
Businesses perform triage by classifying support tickets based on their nature and urgency. For example, they’ll solve high-impact technical problems first to prevent operational issues.
In this blog, we will go over the entire support ticket triage process. We’ll cover:
- What are the types of support tickets?
- How to Triage Support Tickets?
- Benefits of Support Ticket Triage
- Best Practices for Effective Ticket Triage
- Tools for Support Ticket Triage
- Common Challenges in Support Ticket Triage
What are the Types of Support Tickets?
Businesses receive a lot of support queries. You can sort these tickets by nature and by the effort required to solve the tickets. When you know all the types of support tickets, it’s easier to understand support ticket triage.
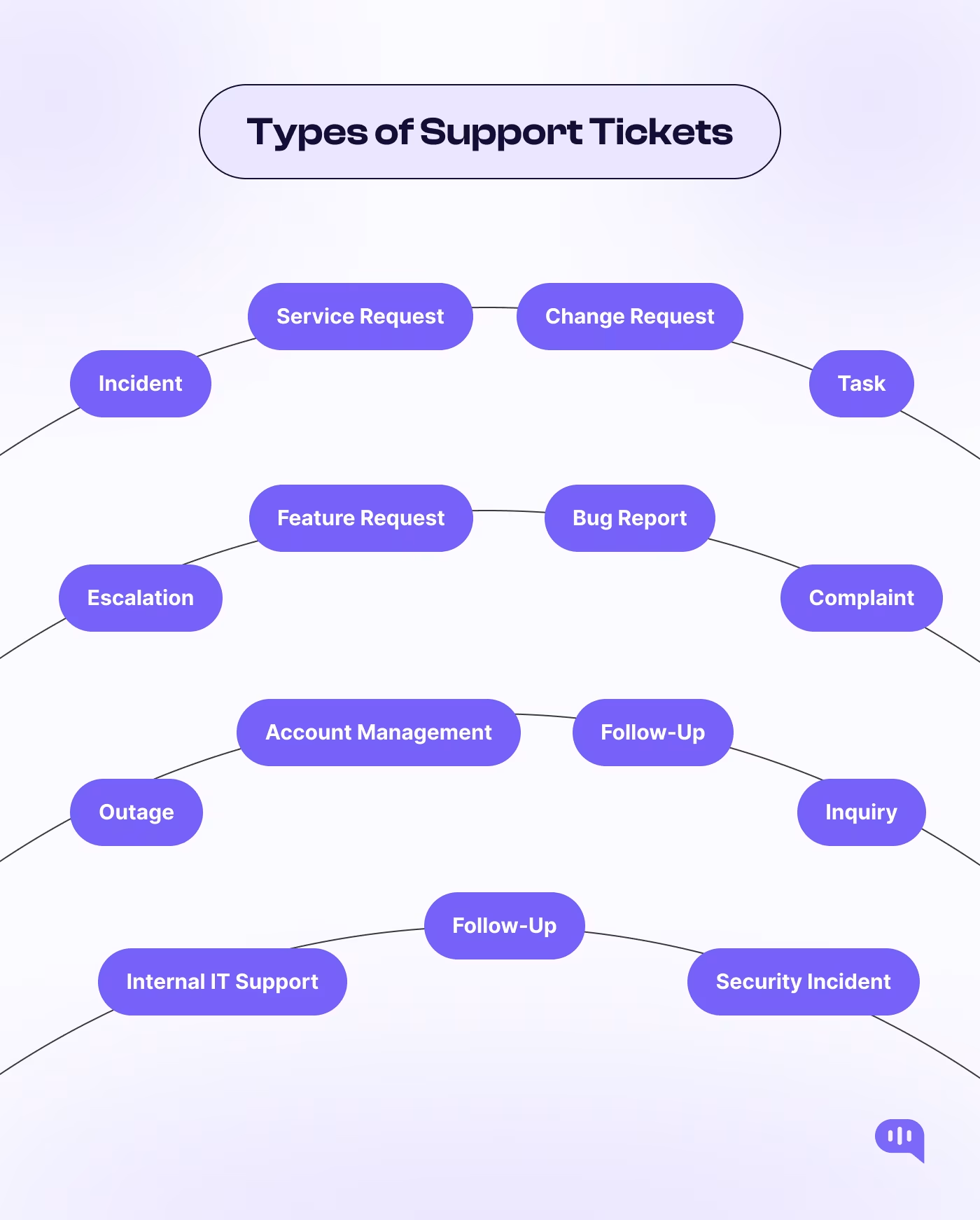
The most common types of support tickets are:
1. Incident Tickets
Technical issues happen when there are software bugs or hardware problems. To solve these tickets, the customer support team has to rely on the tech team.
These issues are usually sent to the tech team through incident tickets. For example, if your servers fail, you would raise an incident ticket and send it to your development team to resolve the problem.
2. Service Request Tickets
A lot of customer questions are about the services your business provides. If a customer asks you for directions on using a service or password reset, this will be filed as a service request ticket.
For example, a client who wants to change their subscription plan will generate a service request ticket.
3. Change Request Tickets
Customers generate change request tickets when they want a new feature enabled in their accounts. This includes requests for new integrations, product updates, and others. Since these tickets influence customer loyalty, they must be prioritized carefully.
For example, a change request ticket is filed when customers want more to enable specific integrations on their account.
4. Problem Tickets
If a specific problem keeps recurring on your product or service, you will raise a problem ticket. Though these tickets deal with technical issues (just like incident tickets), more profound research is needed to solve these problems.
For example, If software cannot read a webpage, a problem with the code might be solved by raising a problem ticket.
5. Task Tickets
Your support team does many tasks throughout the day. Task tickets are used internally to track and prioritize these tasks.
For example, if a support team member analyzes customer data daily, they will have a recurring task ticket on their system.
6. Feature Request Tickets
Customers can submit a feature request ticket when they need a new feature. For example, if many of your customers want an Instagram integration, the development team will put it into the product roadmap.
7. Escalation Tickets
If a customer reports a problem that the support team can’t handle independently, they raise an escalation ticket. These tickets are sent to more senior teams so that they can be solved quickly.
For example, if your customers find an issue with your machines, support team will escalate the ticket to the development team.

8. Bug Report Tickets
If you sell a software product, customers will sometimes report a bug with your product. These complaints are raised as bug report tickets.
For example, it will be reported as a bug if your customers can’t sign in from their phones.
9. Complaint Tickets
Customers unhappy with your product or service can file a complaint ticket. Complaint tickets are used to understand customer sentiment and record their feedback.
For example, if a customer doesn’t like that he had to wait a week for a solution to their problem, they might file a complaint ticket.
10. Outage Tickets
If your customers can’t access a service or product due to server failure or downtime, they will file an outage ticket.
For example, you will file an outage ticket if your website is down.
11. Inquiry Tickets
Whenever a customer asks some questions about your products or services, the questions are counted as inquiry tickets.
For example, If a customer asks about a specific feature, they will file an inquiry ticket.
12. Account Management Tickets
When a particular customer raises a request for their account, it’s filed as an account management ticket. This might include specific data fetch requests or requests to add a new seat to the account.
For example, a customer might request additional overage during black Friday sales and file a account management ticket.
13. Follow-Up Tickets
You raise follow-up tickets when a customer needs more help after the first resolution.
For example, you can create a follow-up ticket to check on a customer after solving a complex technical issue.
14. Internal IT Support Ticket
If your employees face a specific technical issue, an internal IT support ticket is raised.
For example, employees who can’t log into their computers will raise an internal IT support ticket.
15. Security Incident Ticket
Security Incident Tickets are raised when there are cybersecurity issues, data leakage, or other similar problems.
For example, if an unauthorized person accesses your backend, you would raise the security incident ticket.
These types of tickets are commonplace across businesses. And intuitively, you know that some of these tickets will be more critical than others. For example, you must solve account management, security incidents, and incident tickets to help customers and your business.
This is why sorting your tickets into different types helps triage support requests. Now that you understand these categories let’s discuss how you triage support tickets.
How to Triage Support Tickets?
We organize tickets based on how soon they must be solved, how much effort is required, and what their impact is on business. This ensures that high-priority tickets are addressed first.
While still necessary, low-priority tickets have non-time-sensitive queries and can be managed more flexibly.
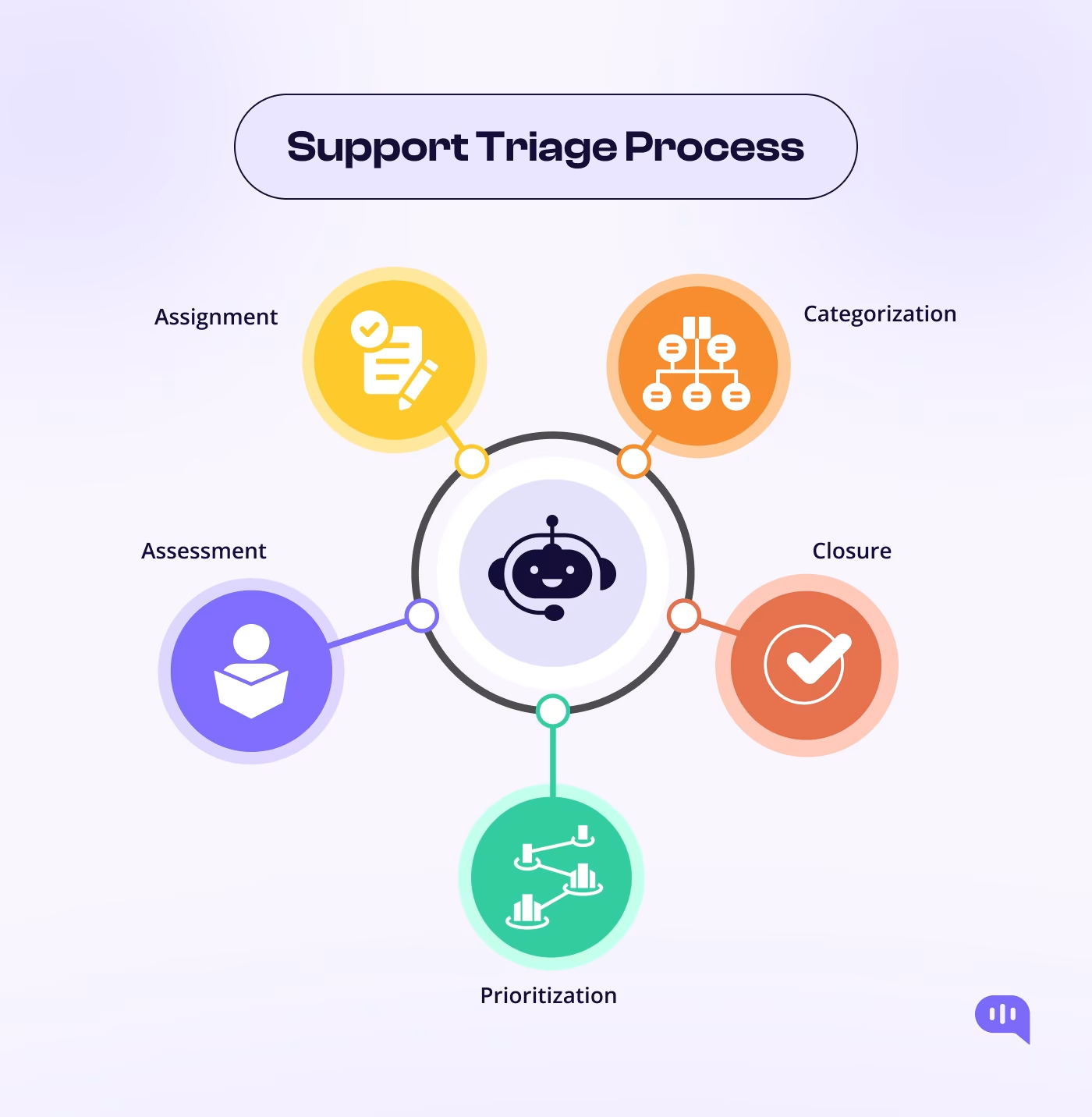
We follow the following steps to sort your tickets into high-priority and low-priority categories.
1. Assessment
First, we need to understand the problem. In this process, the support team looks at the problem and finds out the nature of the issue and relevant information.
For example, if your customers can’t click on a button on your website, the support team will look at why this happens.
2. Categorization
Once you’ve assessed the problem, it’s essential to categorize it into categories. You first need to see which ticket category it falls under and then label it according to severity.
For example, a server disruption will be filed under an “Outage Ticket” and labeled “High Severity.”
3. Prioritization
Tickets are prioritized into two large categories depending on the category and severity. High-priority issues (with higher severity) are dealt with first, and low-priority issues are resolved after.
4. Assignment
Once you’ve assigned priorities to an issue, it’s time to assign it to specific people. The appropriate team is chosen based on the ticket category.
For example, the outage ticket is handed to the server maintenance team.
5. Closure
Once the assigned team solves the problem, the ticket is closed. A report that includes details about the issue and the solution is generated and put along with the resolved ticket.
This process helps businesses manage the high number of tickets they receive daily. Putting this into practice has several benefits. Let’s understand the benefits of this ticket triage system.

What are the Benefits of Support Ticket Triage?
While support ticket triage is usually used to improve workflows and processes in the support function, it also has many other benefits. These are:
1. Higher CSAT Scores – Since support ticket triage directly optimizes the workflow to solve more customer problems, it leads to higher customer satisfaction. Customers get their issues resolved faster and are more satisfied with your business,
2. Improved Workload Distribution – While assigning work during the ticket triage process, you assign work to agents free to take up tasks. This ensures that every agent gets equal workloads and improves employee happiness.
3. Data-Driven Improvements – Since you document every ticket under the support ticket triage system, your team gets access to the latest data on how to solve problems. The documents you make help your team solve recurring issues faster.
4. Streamlined Support Workflow – As we mentioned earlier, support ticket triage helps you streamline the support workflow and helps improve efficiency in your support process.
Now that you understand the how and why of the support triage process, let’s look at some of the best practices that will help you implement.
What are the Best Practices for Effective Ticket Triage?
While every business builds an individual SOP to implement support ticket triage, here are the common themes we’ve found in our research:
1. Clear Categorization
To maintain accuracy, you need to create proper discreet categories. Specific categories around technical outages, customer account requests, and customer inquiries will make your support ticket triage process more efficient.
Most organizations also have predefined operating processes for each category to help streamline their workflows.
2. Urgency Assessment
Create an uniform criteria to understand how urgent a task is. Just like categorization, this will help you prioritize your support tickets better.
Most businesses implement a point-based system to mark tickets with more business impact and customer satisfaction as urgent.
3. Automation
The support ticket triage process must be complemented by automation. Since your team will focus on essential issues, more standard business inquiries and basic service requests should be automated.
Most businesses use some form of FAQ and Gen AI chatbots to automate these repetitive questions and make support ticket triage more efficient.
4. Continuous Improvement
As with most other business decisions, the success of support ticket triage also depends on customer feedback and happiness. So, it’s important to check customer feedback data to find insights. You can then use these insights to improve support ticket categorization and its effectiveness in solving problems.
5. Training and Communication
When establishing a ticket triage workflow in your business, you must conduct thorough training to inform support agents. Create clear training plans and documentation to reduce errors and help maximize the efficiency of the process.
Most businesses implementing these strategies can see triaging success within a few weeks. To help you further, we’ve also listed the tools our clients use to perfect this process.

What Tools Should You Use for Support Ticket Triage?
Various tools are used to incorporate support ticket triage into your support function. Most of our clients use the following systems:
1. Ticketing Systems
Ticketing systems centralize customer communications across multiple channels. They are a central hub through which your support team can manage and track support tickets and assign them.
Many advanced ticketing tools also have systems to automatically assign and resolve conversations, categorize them, and provide real-time updates.
You can use ticketing systems like Freshdesk, Zendesk, Salesforce, etc.
2. Knowledge Management Systems
Internal and external documentation is crucial to making support triage a success. Some tools help you create these databases and structure them well so that your support team and customers can easily find relevant documents.
Some knowledge management systems that you can use are Hubspot, Zendesk Guide, and Salesforce Knowledge.
3. Automation Tools
Automation tools are essential to streamline the support ticket triage process and focus more on critical support tickets. Most businesses use AI-powered email ticketing solutions or an AI customer service chatbot like Kommunicate to streamline support ticket triage processes.
This should help you set up your support ticket triage systems. Now that you know its ins and outs, let’s discuss the most common challenges people face while using and implementing the support triage system.
What are the Common Challenges in Support Ticket Triage?
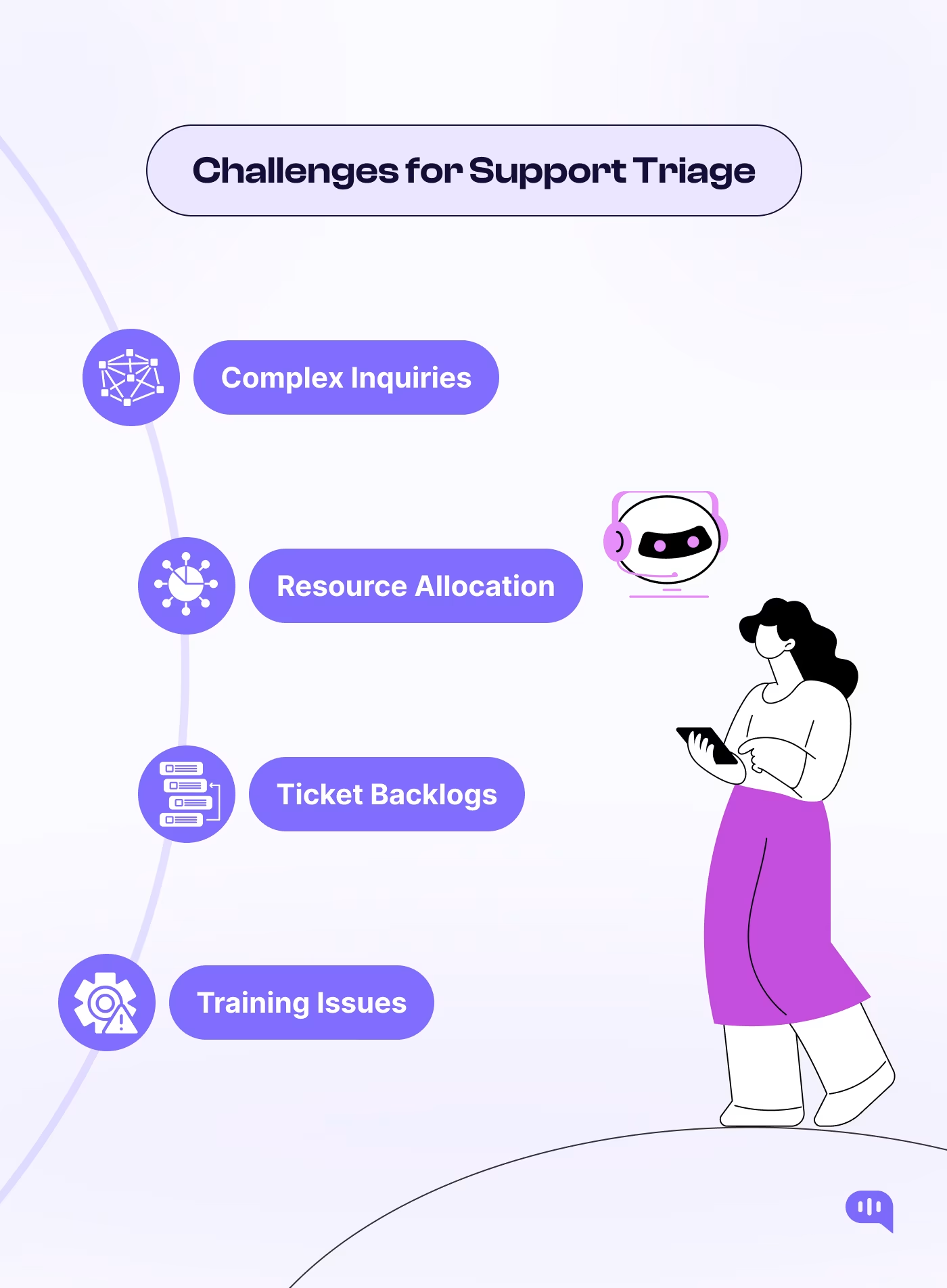
While customer support ticket triage is used across enterprises for workflow management, it still has some prominent challenges. These are:
1. Complex Customer Inquiries
One of the primary challenges is to categorize a customer issue successfully. Since customers can have complex and hard-to-solve problems, organizing them into a single issue becomes difficult. Most businesses break down a customer complaint into parts and raise separate tickets to deal with these complex problems, but it’s still a challenge.
2. Resource Allocation
Another common problem that businesses need is a need for more resources. With most enterprises receiving over 1000 support tickets daily, there needs to be more support agents that can resolve all of them.
This is where automation helps. In our experience, an AI chatbot can reduce incoming inquiries by as much as 65% and help your support agents perform ticket triage more effectively.
3. Handling Backlogs and Ticket Volume
Complex tickets can require multiple days to resolve. This creates a problem because support agents continuously address backlogs while managing new tickets.
Automation reduces the tickets raised for an agent and helps with this problem.
4. Training and Efficiency
Finally, even the most efficient support ticket triage system requires constant training. If agents are not properly trained, they might misassign tickets and cause delays to urgent issues, affecting customer satisfaction and the overall efficiency of your processes.
While resource allocation and ticket volume issues persist even in support ticket triage, using the right automation tools helps. Proper triaging processes with automation help a business improve efficiency and customer satisfaction despite these challenges.
Conclusion
Customer support ticket triage is a process that helps businesses efficiently manage and prioritize their support operations.
To succeed with support triage, you need to focus on the following key elements:
- Clear Ticket Classification: Understanding and organizing the various types of support tickets enables teams to route and handle issues appropriately.
- Systematic Process: Following a structured approach through assessment, categorization, prioritization, assignment, and closure ensures consistent handling of customer issues.
- Tangible Benefits: Support triage delivers multiple advantages, including improved customer satisfaction scores, balanced workload distribution, data-driven insights, and streamlined workflows.
- Best Practices: Implementing precise categorization, proper urgency assessment, automation integration, continuous improvement, and thorough team training are essential for successful triage implementation.
- Proper Tools: Utilizing appropriate ticketing systems, knowledge management platforms, and automation tools helps optimize the triage process and improve overall efficiency.
While challenges like complex inquiries, resource constraints, and ticket backlogs exist, organizations can overcome these obstacles by properly implementing automation tools and well-defined processes. The key is to balance efficient ticket management with maintaining high-quality customer support.
As businesses grow and customer expectations evolve, support ticket triage remains crucial for delivering exceptional customer service while managing resources effectively. By following this article’s guidelines and best practices, organizations can build a robust support ticket triage system that benefits their customers and support teams.

As a seasoned technologist, Adarsh brings over 14+ years of experience in software development, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to his role. His expertise in building scalable and robust tech solutions has been instrumental in the company’s growth and success.